How To Manage or Prevent Psoriasis
How To Manage or Prevent Psoriasis –
Effective Strategies To Treat Psoriasis:
Psoriasis Overview
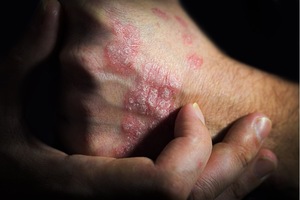
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin. It is characterized by the rapid growth of skin cells that accumulate on the skin’s surface, leading to the formation of red, itchy, scaly patches. Psoriasis can occur anywhere on the body, but it is most commonly found on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. This article seaks to inform you about the best tactics to manage or even prevent psoriasis.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, including plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis. Plaque psoriasis is the most common type and is characterized by red, raised patches covered with a silvery white buildup of dead skin cells.
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to be related to an immune system malfunction. In people with psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing the rapid growth of new skin cells. This leads to the formation of the characteristic red, itchy, scaly patches.
Risk Factors for Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis
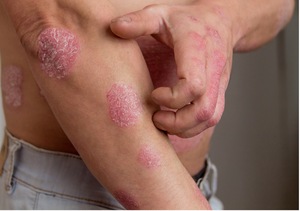 Several factors can increase a person’s risk of developing psoriasis, including genetics, environmental factors, and lifestyle factors. People with a family history of psoriasis are more likely to develop the condition themselves. Environmental factors, such as stress, infections, and injuries to the skin, can trigger psoriasis flare-ups. Lifestyle factors, such as smoking and obesity, can also increase the risk of developing psoriasis.
Several factors can increase a person’s risk of developing psoriasis, including genetics, environmental factors, and lifestyle factors. People with a family history of psoriasis are more likely to develop the condition themselves. Environmental factors, such as stress, infections, and injuries to the skin, can trigger psoriasis flare-ups. Lifestyle factors, such as smoking and obesity, can also increase the risk of developing psoriasis.
Psoriasis Affects any part of the body
Psoriasis can affect any part of the body, including the feet, hands, face, and genitals. On the feet Psoriasis can cause discomfort and difficulty walking, while psoriasis on the hands can interfere with daily activities. On the face it can be particularly distressing, as it can affect a person’s self-esteem and quality of life. Genital psoriasis can cause discomfort and embarrassment and may require specialized treatment. It is important to distinguish between psoriasis and eczema, as they are two different conditions that require different treatments.
RELATED ARTICLE: Beat Eczema Skin Problems Now
How To Manage or Prevent Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that can be managed with proper treatment and prevention measures. Prevention measures can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Here are some ways to prevent psoriasis:
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can help prevent psoriasis. Here are some lifestyle changes that can be made:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Get enough sleep
Dietary Changes
Dietary changes can also help prevent psoriasis. Here are some dietary changes that can be made:
- Eat a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and foods high in saturated and trans fats
- Consider taking vitamin D3 and omega-3 supplements
Stress Management
Stress can trigger psoriasis flare-ups. Here are some ways to manage stress:
- Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga
- Get regular exercise
- Take breaks throughout the day to relax and recharge
- Seek professional help if needed
By making these lifestyle, dietary, and stress management changes, individuals with psoriasis can help prevent flare-ups and improve their overall quality of life.
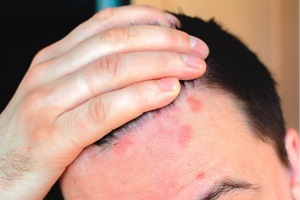 Is Psoriasis Curable?
Is Psoriasis Curable?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that can be managed but not cured. The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation, relieve symptoms, and prevent complications. Treatment options depend on the severity and location of psoriasis, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences. A dermatologist can help determine the best treatment plan for each individual.
Topical Psoriasis Treatments
There are psoriasis creams, psoriasis ointments, and psoriasis medications.available Topical treatments are applied directly to the skin and are often the first line of defense for mild to moderate psoriasis. They can reduce inflammation, itching, and scaling, and may be used alone or in combination with other therapies. Examples of topical treatments include:
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory drugs come in various strengths and forms, such as creams, ointments, lotions, gels, and foams. They are most effective for short-term use on limited areas of the body, as long-term use can cause skin thinning, discoloration, and other side effects.
- Vitamin D analogues: These synthetic compounds mimic the effects of natural vitamin D on the skin, which can slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation. They are available as creams, ointments, and solutions, and may be used alone or in combination with corticosteroids.
- Retinoids: These vitamin A derivatives can normalize skin cell growth and reduce inflammation, but they can also cause skin irritation, dryness, and sun sensitivity. They are available as gels, creams, and solutions, and are often used in combination with other topical treatments.
- Salicylic acid: This keratolytic agent can soften and remove scales, but it can also irritate the skin and cause dryness. It is often used in combination with other topical treatments.
Systemic Medications to Manage or Prevent Psoriasis
Systemic medications are taken orally or by injection and are reserved for severe or widespread psoriasis that cannot be controlled by topical treatments. They work by suppressing the immune system, reducing inflammation, or targeting specific molecules involved in psoriasis. Examples of systemic medications include:
- Methotrexate: This immunosuppressant drug can slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation, but it can also cause liver damage, bone marrow suppression, and other serious side effects. It requires regular monitoring of blood tests and should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Cyclosporine: This immunosuppressant drug can relieve symptoms quickly but should not be used for long periods due to the risk of kidney damage, high blood pressure, and other side effects. It requires regular monitoring of blood tests and should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Biologics: These targeted therapies block specific molecules involved in psoriasis, such as TNF-alpha, IL-17, or IL-23, and can provide long-lasting relief with fewer side effects than traditional immunosuppressants. They are administered by injection or infusion and may require regular monitoring of blood tests and TB screening.
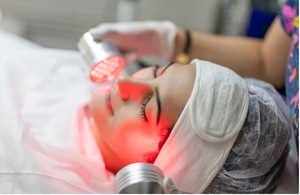 Light Therapy
Light Therapy
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, uses specific wavelengths of ultraviolet (UV) light to slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation. It can be used alone or in combination with topical or systemic treatments and requires regular monitoring by a dermatologist. Examples of light therapy include:
- UVB therapy: This type of light therapy uses a specific wavelength of UVB light to treat psoriasis and can be administered at home or in a clinic. It can cause sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer if not used properly and should be avoided during pregnancy.
- PUVA therapy: This type of light therapy combines UVA light with a photosensitizing drug called psoralen, which makes the skin more sensitive to light. It can be effective for severe psoriasis but requires strict sun protection and can cause nausea, headaches, and other side effects.
Alternative Therapies to Manage or Prevent Psoriasis
Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, aromatherapy, herbal supplements, and dietary changes, are not supported by strong scientific evidence and should be used with caution. Some may interact with medications or cause allergic reactions, and others may be ineffective or even harmful. However, some people with psoriasis may find relief from stress reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or tai chi, or from dietary changes that eliminate gluten, dairy, or other trigger foods. It is important to discuss any alternative therapies with a healthcare provider before trying them.
Psoriasis Self-Care
Individuals with psoriasis can benefit from self-care practices to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Self-care practices can include bathing and moisturizing, avoiding triggers, and managing itching and discomfort.
 Bathing and Moisturizing
Bathing and Moisturizing
Bathing can help remove scales and soothe itching, but it is important to avoid hot water and harsh soaps, which can worsen symptoms. Instead, individuals with psoriasis should use lukewarm water and mild, fragrance-free soaps. Adding bath oils or colloidal oatmeal can also help soothe the skin.
After bathing, individuals with psoriasis should pat their skin dry and apply a moisturizer to help lock in moisture. Thick, fragrance-free creams or ointments can be particularly helpful for those with psoriasis. Moisturizing regularly can help reduce dryness and itching, and may even help prevent psoriasis flares.
Avoiding Triggers
Certain triggers can worsen psoriasis symptoms, so it is important to identify and avoid them whenever possible. Common triggers can include stress, infections, injury to the skin, alcohol, smoking, and certain medications.
Individuals with psoriasis should work with their healthcare provider to identify their triggers and develop a plan to avoid or manage them. Keeping a journal to track symptoms and potential triggers can also be helpful.
Managing Itching and Discomfort
Itching and discomfort are common symptoms of psoriasis, but there are several self-care practices that can help manage them. Applying cool compresses or taking a cool bath can help soothe itching. Over-the-counter anti-itch creams or ointments can also be helpful for some individuals.
In addition, stress reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help manage stress and reduce itching and discomfort. Finally, wearing soft, loose clothing and avoiding scratchy fabrics can help reduce irritation and itching.
Self-care practices can be an important part of managing psoriasis symptoms and improving quality of life. By following these tips and working with their healthcare provider, individuals with psoriasis can develop a self-care plan that works for them.
 How To Manage Or Prevent Psoriasis:
How To Manage Or Prevent Psoriasis:
Questions and Answers
Managing or Preventing Psoriasis can become all encompassing, do not let it take over your life! Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, causing it to become red, itchy, and scaly.
Here are some common questions and answers about psoriasis management, prevention and treatment:
- What causes psoriasis? The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to be related to an immune system problem. Certain factors, such as stress, infections, and certain medications, can trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms.
- Is psoriasis contagious? No, psoriasis is not contagious. It is a non-infectious condition that cannot be spread from person to person.
- Can psoriasis be prevented? While there is no known way to prevent psoriasis, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of flare-ups. These include avoiding triggers such as stress, smoking, and alcohol, and taking good care of the skin by moisturizing regularly and avoiding harsh soaps and detergents.
- What are the treatment options for psoriasis? Treatment for psoriasis depends on the severity of the condition and the individual’s symptoms. Options include topical treatments such as creams and ointments, phototherapy (light therapy), and systemic medications such as biologics and oral medications.
- Are there any natural remedies for psoriasis? While there is no cure for psoriasis, some people find relief from symptoms by using natural remedies such as aloe vera, tea tree oil, and turmeric. However, it is important to talk to a healthcare provider before using any natural remedies, as some may interact with medications or cause allergic reactions.
- Can psoriasis lead to other health problems? In some cases, psoriasis may be associated with other health problems such as arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and depression. It is important for individuals with psoriasis to work closely with their healthcare provider to monitor their overall health and manage any related conditions.
Recent Developments (2023)
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently approved a new drug for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. The drug, Deucravacitinib, is the first TYK2 inhibitor to be approved for the treatment of any disease. It will be sold with the brand name Sotyktu
- The FDA recently approved tapinarof (VTAMA; Dermavant) cream 1%, a once-daily, steroid-free topical treatment for plaque psoriasis in adults – regardless of the severity of their disease. This is the first FDA-approved steroid-free topical medication for psoriasis.